Sweet Potato Nutrition: Calories & Health Benefits
What if one of the healthiest foods you could eat was already sitting in your kitchen? Sweet potato nutrition has become a hot topic in health and wellness circles — and for good reason. Packed with complex carbs, antioxidants, and gut-friendly fiber, sweet potatoes offer far more than just a sweet taste.
Understanding sweet potato nutrition can help you make smarter food choices, whether you’re aiming to manage blood sugar, lose weight, or simply eat more whole, fiber-rich foods. This root vegetable isn’t just delicious — it’s nutrient-dense, budget-friendly, and incredibly versatile.
From supporting immunity to keeping you full longer, the health benefits of sweet potatoes are hard to ignore. And the best part? They’re easy to cook and even easier to love.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about sweet potato nutrition, from calorie counts and vitamins to preparation tips that preserve nutrients. Let’s dive in.
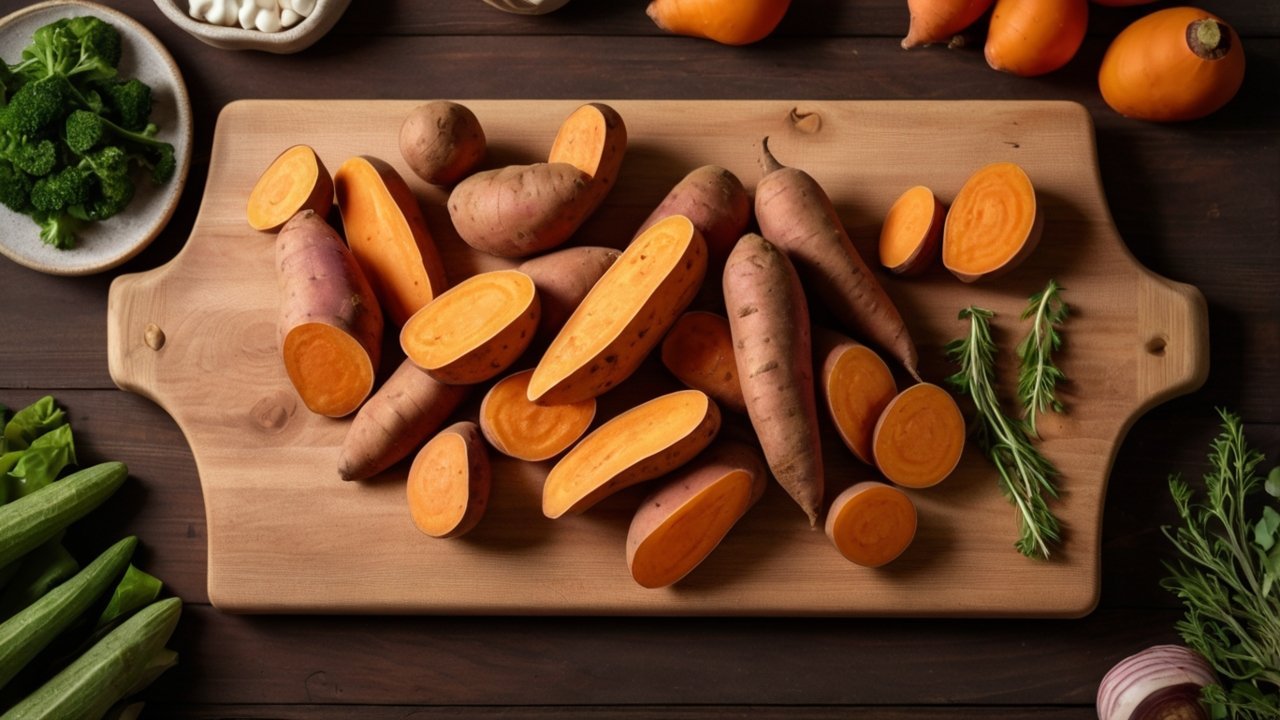

Chapter 1: Why Sweet Potatoes Deserve a Spot on Your Plate
Sweet Potato Nutrition: A Superfood with Substance
Let’s get one thing clear: sweet potato nutrition isn’t hype — it’s backed by science. Whether you’re tracking macros, boosting immunity, or just trying to avoid the 3 p.m. crash, sweet potatoes belong in your kitchen.
Here’s why.
A Nutrient Powerhouse in Every Bite
Sweet potatoes are more than “just carbs.” They’re rich in:
-
Complex carbohydrates for steady energy (no sugar spike).
-
Dietary fiber (3.3g per 100g cooked) to support digestion.
-
Vitamin A (from beta-carotene) – one of the highest sources among veggies.
-
Potassium – even more than a banana.
-
Vitamin C, B6, and small but significant amounts of iron and magnesium.
👉 According to a Harvard Health review, beta-carotene from sweet potatoes may help reduce the risk of certain cancers and improve immune function.
A Healthier Carb for Real Life Goals
Let’s face it — not everyone wants to live off kale and quinoa. Sweet potatoes hit the sweet spot: comfort food that doesn’t compromise your goals.
Compare this:
-
White potato (boiled, 100g): ~87 calories, 0.1g fat, 1.9g fiber
-
Sweet potato (boiled, 100g): ~76 calories, 0.1g fat, 3.3g fiber
Plus, the lower glycemic index (GI) of sweet potatoes makes them a smarter choice for blood sugar control — especially important for people managing diabetes.
👉 For related insights, check out our 2025 Diabetes Management Guide.
Why Fitness Enthusiasts Swear by Sweet Potatoes
Athletes and bodybuilders love sweet potatoes for good reason:
-
Long-lasting energy for workouts
-
High satiety for fat-cutting phases
-
Supports muscle recovery thanks to antioxidants
💪 Want to pair your diet with high-protein options? Don’t miss our 2025 Protein Guide + Meal Plan.
Story Time: From Cravings to Clean Energy
Sophie, a fitness coach and mom of two, used to crash after lunch—then reach for sugary snacks. Once she swapped white rice and bread for roasted sweet potatoes in her meal prep, her afternoons shifted from sleepy to productive.
“I feel full longer, no cravings, and I’ve lost 6 lbs without even trying,” she said.
This isn’t magic. It’s sweet potato nutrition in action.
Pros and Cons: Be Smart, Not Blind
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Nutrient-dense and fiber-rich | Can be high in carbs for strict keto diets |
| Supports blood sugar regulation | Overcooking reduces vitamin content |
| Affordable, versatile, accessible | Needs portion control for weight loss |
👉 Looking to cut bloating while increasing fiber naturally?
Read about the trending FibreMaxxing gut health strategy.
Best Solution for Busy People: Meal Prep + Sweet Potato
Need quick wins? Bake or boil sweet potatoes in batches. Store them in glass containers for:
-
Breakfast bowls
-
Post-workout meals
-
Quick work-from-home lunches
💡 Looking for a gut-friendly solution that works with sweet potato-heavy diets?
Check this recommended tool here → LeanBiome
Discover This Affordable Superfood Today
Compared to supplements or niche “superfoods,” sweet potatoes are:
-
Widely available
-
Budget-friendly
-
Kid- and elder-approved
If you’re building a foundation of real, functional nutrition, this is it.
✨ See pricing and reviews on the official site → LiveSmart Health Superfoods
🧠 Real-World Takeaway: Don’t Overthink, Just Start
You don’t need a perfect diet — you need better building blocks. Swapping one refined carb for sweet potato can:
-
Improve digestion
-
Support immunity
-
Boost energy without jitters
Want to pair sweet potatoes with clean protein?
Try our Healthy Chicken Recipes for Fitness for meal inspiration.
🔗 Internal Links Used:

Chapter 2: Sweet Potato Nutrition Facts (Per 100g, Cooked)
How healthy is a sweet potato really? Here’s the full nutritional breakdown.
🥄 Sweet Potato Nutrition: The Real Numbers
If you’ve ever wondered exactly what’s inside a sweet potato, you’re not alone. This humble root veggie is often labeled a “superfood” — and for good reason. But today, we go past the hype and dive into data-backed facts.
So, per 100g of cooked sweet potato (boiled, without skin), here’s what you’re actually getting:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | ~86 kcal |
| Carbohydrates | ~20g |
| Dietary Fiber | ~3.3g |
| Sugars | ~4.2g |
| Protein | ~1.6g |
| Fat | ~0.1g |
| Vitamin A (RAE) | ~961 µg (over 100% DV) |
| Vitamin C | ~2.4 mg |
| Potassium | ~337 mg |
| Manganese | ~0.5 mg |
| Magnesium | ~25 mg |
📌 Source: USDA FoodData Central
🔍 Sweet Potato vs. Other Staples: A Quick Comparison
| Sweet Potato (100g) | White Potato (100g) | Brown Rice (100g cooked) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 86 kcal | 87 kcal | 111 kcal |
| Carbs | 20g | 20g | 23g |
| Fiber | 3.3g | 1.8g | 1.8g |
| Vitamin A | 100%+ DV | ~0% | ~0% |
✔️ Verdict: Sweet potatoes outperform on fiber and micronutrients — especially Vitamin A and manganese.
👉 If you’re interested in nutrient-dense alternatives, you might also like our Banana Nutrition Facts Guide.
🍠 Top Micronutrients in Sweet Potatoes (and What They Actually Do)
🔸 Vitamin A (Beta-Carotene)
-
Supports immune function, vision, and skin health
-
Helps reduce inflammation
-
Pro tip: Eat sweet potatoes with a little healthy fat (like olive oil) to enhance absorption.
🔸 Potassium
-
Regulates fluid balance and blood pressure
-
Aids in muscle contraction and nerve function
-
Sweet potatoes have more potassium than bananas!
🔸 Fiber
-
Improves digestion
-
Helps manage blood sugar spikes
-
Keeps you feeling full longer
🔗 Want to double down on gut health? Try the FibreMaxxing trend.
🩸 Sweet Potato Glycemic Index: What You Need to Know
The glycemic index (GI) of boiled sweet potatoes ranges between 44–61, making them a low to medium GI food.
This means they:
-
Cause slower blood sugar release
-
Are safer for those with insulin resistance or diabetes
-
Offer more stable energy levels
⚠️ Note: Baking or frying sweet potatoes can increase their GI — so how you cook them matters.
👉 For guidance on blood sugar-friendly diets, see our 2025 Diabetes Management Guidelines.
💬 Real Talk: Is More Always Better?
While sweet potato nutrition is impressive, balance is still key. Too much of anything — even something healthy — can work against your goals.
👍 When Sweet Potatoes Shine:
-
Pre/post-workout meals
-
Meal prep for weight loss
-
Gut health resets
-
Plant-based diets
⚠️ When to Moderate:
-
Strict keto diets
-
People with severe IBS (may trigger FODMAP issues)
-
Carb-sensitive individuals
Need low-carb swaps? Check out our Caffeine-Free Coke Alternatives for smart replacements.
🔗 Affiliate CTA: Sweet Potato-Friendly Meal Support
Eating clean is easier with the right nutritional tools.
For people focusing on gut reset or weight loss support, this is a game-changer:
✅ Discover this affordable solution today → LeanBiome
(Supports gut flora and digestion – works well with fiber-rich foods like sweet potatoes.)
🧠 Pro Tips to Maximize Nutrient Retention
-
Boil or steam instead of frying
-
Leave skin on (if organic) for extra fiber
-
Pair with healthy fats (avocado, nut butter, olive oil)
-
Avoid sugar-loaded preparations (marshmallow casseroles = no thanks)
🔗 Internal Links Used:

Chapter 3: Key Health Benefits of Sweet Potatoes
Why this root vegetable goes beyond basic carbs.
🌿 Sweet Potato Nutrition Benefits: Backed by Science
Sweet potatoes aren’t just “healthy carbs.” Their unique mix of micronutrients, antioxidants, and fiber makes them a powerful addition to nearly any wellness plan — from weight loss to gut repair to immune support.
In this section, we’ll break down the top 5 sweet potato health benefits, show you where they really shine, and recommend tools to help you get the most out of every bite.
🧬 1. Sweet Potatoes Boost Immune Function & Eye Health
The orange flesh of a sweet potato is loaded with beta-carotene, a plant compound your body converts into Vitamin A — an essential micronutrient for:
-
Strengthening immune responses
-
Reducing inflammation
-
Supporting mucous membrane health (your body’s natural shield)
-
Maintaining good vision and preventing age-related eye decline
📌 A study from PubMed found that beta-carotene-rich diets significantly improve markers of immune defense — particularly in older adults.
🧠 Quick Tip: You absorb more beta-carotene when sweet potatoes are cooked and paired with a fat source (like olive oil or avocado).
🧘 2. They Support Gut Health and Regularity
Sweet potatoes are rich in soluble and insoluble fiber, which:
-
Feeds good gut bacteria (prebiotic effect)
-
Improves stool consistency and motility
-
Reduces bloating and constipation
-
May help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract
A diet high in fiber like that from sweet potatoes can even lower the risk of colon cancer over time.
👉 Want to improve digestion while reducing gas and bloating?
Check this recommended tool here → LeanBiome
(Trusted by over 40,000 users for gut balance and weight control.)
Also, read our deep dive on the FibreMaxxing gut health trend to optimize your fiber game.
⚖️ 3. Sweet Potatoes Can Help With Weight Management
Because of their low calorie density and high fiber content, sweet potatoes:
-
Keep you full longer
-
Reduce the urge to snack
-
Stabilize blood sugar
-
Provide sustained energy with fewer cravings
This makes them ideal for fat-loss-focused diets. A medium sweet potato has fewer than 110 calories, but delivers big on satiety and satisfaction.
👟 Trying to cut stubborn belly fat? Pair sweet potatoes with these at-home fat-burning exercises.
🛒 Or try HepatoBurn, a metabolism support formula many readers combine with high-fiber foods:
See pricing and reviews on the official site → HepatoBurn
❤️ 4. They’re Naturally Anti-Inflammatory
Sweet potatoes are rich in polyphenols, vitamin C, and choline — all of which play a role in reducing inflammation.
Chronic inflammation is linked to:
-
Heart disease
-
Obesity
-
Brain fog
-
Premature aging
A review from Healthline also highlights the anti-inflammatory effects of anthocyanins found in purple sweet potatoes — which may improve brain function and memory.
📌 For a full anti-inflammatory lifestyle overhaul, check out our Top Superfoods for Energy & Fat Burn.
💪 5. Sweet Potatoes Fuel Performance and Recovery
Their potassium, manganese, and complex carbs make sweet potatoes ideal for:
-
Pre-workout fueling
-
Muscle recovery post-training
-
Reducing exercise-induced inflammation
That’s why athletes often choose sweet potatoes over plain white rice or bread — especially during training cycles.
Want a high-protein companion dish? Grab ideas from our Healthy Chicken Recipes for Fitness.
🟢 Realistic, Evidence-Based Recap
| Benefit | Backed By | Practical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Immune boost | Harvard Health, PubMed | Eat 2–3x/week with olive oil |
| Gut health | Gut microbiome studies | Pair with probiotics & hydration |
| Weight management | Satiety/fiber research | Use in meal prep, control portions |
| Anti-inflammatory power | Polyphenol & anthocyanin data | Rotate with purple varieties weekly |
| Performance/recovery boost | Sports nutrition research | Include pre-/post-workout meals |
💡 How to Maximize These Health Benefits
-
Boil instead of deep-fry to preserve antioxidants
-
Rotate colors (orange + purple) for broader polyphenol intake
-
Watch your portion size if tracking carbs or insulin sensitivity
-
Add herbs like turmeric or cinnamon to enhance anti-inflammatory effects
🔗 Internal Links Used:
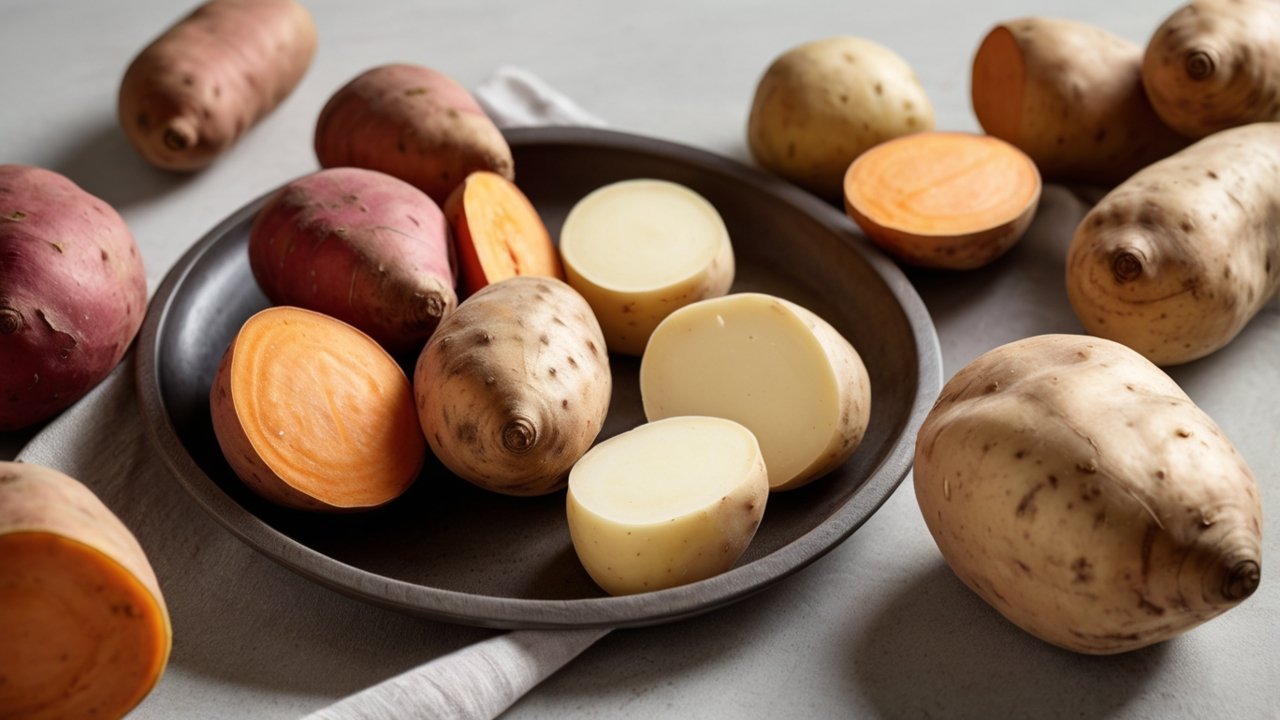

Chapter 4: Sweet Potatoes vs. White Potatoes – Which Is Healthier?
Breaking down the battle of the spuds with facts, not fluff.
🥔 Potato Showdown: The Classic vs. The Superfood
White potatoes are a staple. Sweet potatoes are a trend. But which actually delivers more in terms of health, energy, and real-world impact?
Let’s unpack the nutritional profiles, glycemic impact, and dietary use cases — so you can make smarter food decisions that actually stick.
🔬 Nutritional Comparison: Sweet Potato vs White Potato
| Nutrient (100g, boiled) | Sweet Potato | White Potato |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 86 kcal | 87 kcal |
| Carbs | 20g | 20g |
| Fiber | 3.3g | 1.8g |
| Sugar | 4.2g | 0.8g |
| Protein | 1.6g | 1.9g |
| Vitamin A | 961 µg (100%+ DV) | ~0 µg |
| Potassium | 337 mg | 379 mg |
| Vitamin C | 2.4 mg | 13 mg |
| Glycemic Index (boiled) | ~44–61 | ~78–85 |
Quick Verdict:
-
Sweet potatoes win in fiber, Vitamin A, and glycemic control.
-
White potatoes are slightly higher in Vitamin C and potassium, but also spike blood sugar more.
👉 Want to boost immunity and reduce inflammation naturally?
Check out our Top Superfoods Guide to build your own nutrient-rich plate.
⚖️ Weight Loss & Satiety: Which Potato Keeps You Full Longer?
Sweet potatoes are naturally more filling thanks to:
-
Higher fiber content
-
Lower glycemic load
-
Slower digestion rate
This helps curb cravings and reduce snacking between meals. That’s why many meal prep enthusiasts and athletes opt for sweet potatoes in cutting phases.
🛒 Want to accelerate fat burn with your diet?
See how HepatoBurn complements sweet potato-based meal plans → Check pricing here
🩸 Blood Sugar Control: A Critical Difference
If you’re watching your blood sugar — whether managing prediabetes, insulin resistance, or full-blown type 2 diabetes — sweet potatoes are the clear winner.
| Glycemic Index (GI) | GI Range |
|---|---|
| Sweet Potato (boiled) | 44–61 (low/med) |
| White Potato (boiled) | 78–85 (high) |
| White Potato (baked) | Up to 111 |
Boiled sweet potatoes have a low-to-moderate GI, while white potatoes — especially baked or mashed — spike blood sugar quickly.
📌 According to Harvard Health, lower GI foods help with weight loss, insulin control, and even lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
👉 Learn more in our 2025 Diabetes Management Guide.
💪 Workout Fuel: Which Potato Wins on Performance?
Before workouts:
-
Sweet potatoes offer sustained energy with fiber and antioxidants.
-
Lower risk of energy crash mid-session.
After workouts:
-
White potatoes deliver fast-digesting carbs — helpful for glycogen replenishment (especially for endurance athletes).
👊 Want a complete recovery + clean eating setup?
Check our High-Protein Diet Guide 2025 and pair it with sweet potato-based meals.
🧠 Cognitive & Anti-Inflammatory Benefits
Purple sweet potatoes (yes, they exist) contain anthocyanins, which are powerful brain-boosting antioxidants. White potatoes? Not so much.
These compounds:
-
Fight oxidative stress
-
Improve memory and focus
-
May help reduce cognitive decline with age
📌 Healthline confirms the anti-inflammatory edge of sweet potatoes, especially the colored varieties.
🔄 When White Potatoes Might Still Be the Best Choice
Let’s keep it real — white potatoes aren’t “bad.” They can be beneficial when:
-
You need quick carbs for energy
-
Budget is tight (they’re cheaper)
-
You eat the skin (added fiber and potassium)
-
You’re on a bulking or high-calorie diet
But if your goal is stable energy, gut health, or fat loss, sweet potatoes are the better solution.
🛠️ Recommended Tools for Sweet Potato-Based Nutrition
Need a metabolism boost or gut support to go with your sweet potato meals?
-
LeanBiome for gut-flora balance:
Check this recommended tool here → LeanBiome Affiliate Link -
LiveSmart Health Superfood Kits:
See pricing and reviews on the official site → LiveSmart Health
✅ Summary Table: Sweet vs. White Potato
| Feature | Sweet Potato | White Potato |
|---|---|---|
| Calories (100g) | ~86 | ~87 |
| Fiber | ✅ Higher (3.3g) | ❌ Lower (1.8g) |
| Vitamin A | ✅ 100%+ DV | ❌ None |
| Glycemic Index | ✅ Lower | ❌ Higher |
| Satiety | ✅ Longer-lasting | ⚠️ Shorter-lived |
| Blood Sugar Impact | ✅ Mild | ❌ High |
| Workout Fuel (Pre) | ✅ Yes | ⚠️ Risk of crash |
| Budget Friendly | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
🔗 Internal Links Used:
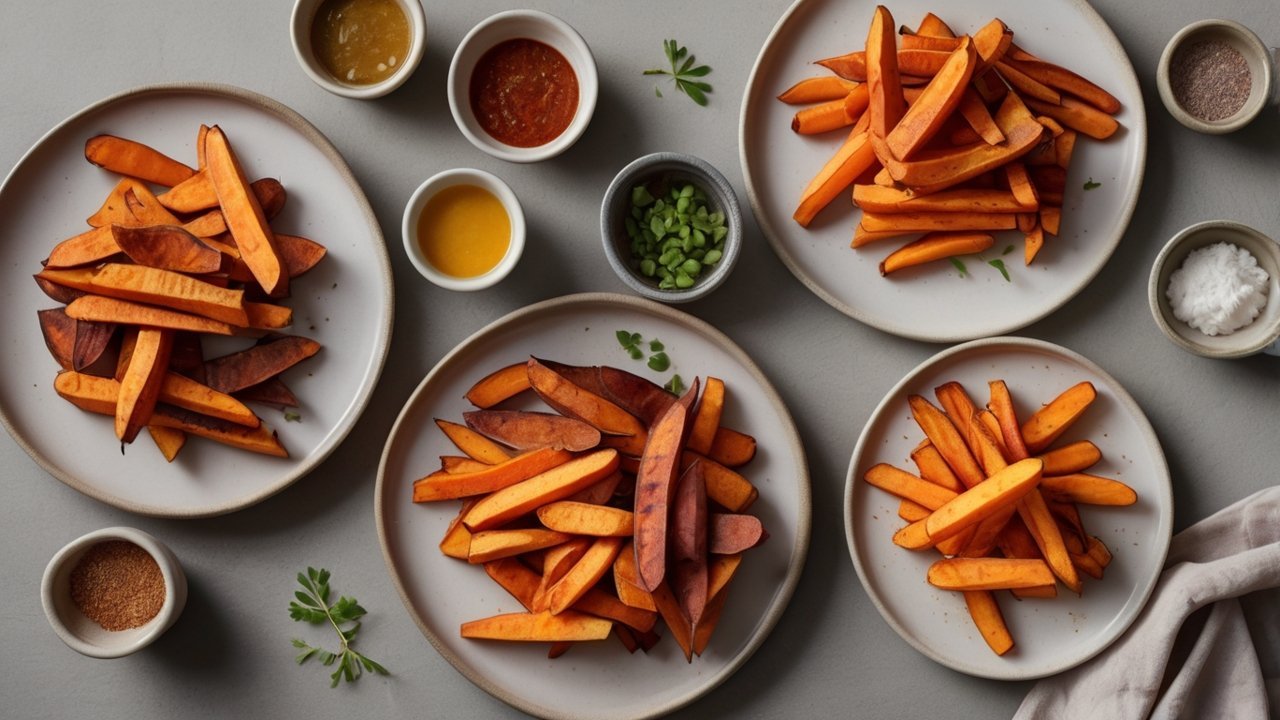

Chapter 5: Best Ways to Prepare Sweet Potatoes (Without Losing Nutrients)
Maximize taste. Preserve the nutrition. Here’s how.
🍽️ Why Cooking Method Matters in Sweet Potato Nutrition
You’ve stocked up on sweet potatoes… now what?
Here’s the twist most people miss: how you cook your sweet potatoes can significantly change their nutritional impact.
Certain methods enhance their health benefits, while others can turn them into blood-sugar-spiking starch bombs. This chapter shows you the best cooking techniques, when to use each, and how to avoid common nutrient-killing mistakes.
🔥 1. Boiling: The Best Method for Blood Sugar Stability
Boiling is one of the healthiest and most underrated methods. It keeps the glycemic index (GI) lower than baking or roasting, making it the top choice for those managing diabetes, weight, or blood sugar spikes.
| Method | GI Value |
|---|---|
| Boiled | 44–61 |
| Baked | 86–94 |
| Fried | 76+ |
Benefits:
-
Preserves vitamin A and C better than frying
-
Keeps calories low
-
Retains moisture and soft texture
💡 Tip: Boil with skin on to preserve nutrients, then peel before serving.
👉 Managing diabetes or insulin resistance? Check out our 2025 Diabetes Management Guide.
🔥 2. Baking: Best for Flavor & Meal Prep
Baked sweet potatoes are a crowd favorite — especially for meal prep, lunch bowls, or post-workout carbs.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Deep flavor | Higher GI than boiling |
| Easy to batch cook | Some vitamin loss due to heat |
| Great for roasting whole or sliced | May dry out if overbaked |
🛠 Recommended tool: Want crisp edges without deep frying?
Check this affordable solution today → LiveSmart Health Air Fryer Picks
🔥 3. Steaming: Best for Maximum Nutrient Retention
Steaming may not be as sexy as roasting, but it’s one of the healthiest cooking techniques available.
Why it works:
-
Minimizes nutrient loss (especially vitamin C and potassium)
-
Retains texture without drying
-
Excellent for baby food, smoothies, and low-fat diets
💡 Pro tip: Add a pinch of sea salt and cinnamon post-steam to enhance flavor without calories.
👉 Want more low-fat nutrition hacks? Don’t miss our Top Superfoods for Energy & Fat Burn.
⚠️ 4. Frying: The Worst for Sweet Potato Nutrition
Deep frying sweet potatoes creates a crispy texture — but at a cost.
-
Adds excessive calories and unhealthy fats
-
Reduces antioxidant levels
-
Spikes glycemic index and insulin response
Verdict: Occasional treat? Sure. Everyday habit? Not ideal.
Want a gut-friendly reset instead?
Check this recommended tool here → LeanBiome
🍳 5. Quick Guide: Cooking Method vs Health Goal
| Goal | Best Cooking Method |
|---|---|
| Blood sugar stability | Boiling |
| Maximum nutrients | Steaming |
| Best taste + versatility | Baking or Roasting |
| Weight loss | Steaming or Boiling |
| Meal prep | Baking |
| Gut health | Steaming + probiotic pairing |
👉 Want easy fitness meals with sweet potatoes? Check out our Healthy Chicken Recipes.
🧪 Cooking Tips to Preserve Sweet Potato Nutrition
✅ Leave the skin on during cooking to keep fiber and micronutrients intact
✅ Avoid overcooking, especially in the oven — it destroys vitamin A
✅ Pair with a healthy fat like olive oil to boost beta-carotene absorption
✅ Add anti-inflammatory spices like turmeric, cumin, or paprika
✅ Batch cook and store in airtight glass containers for the week
Need an energy-boosting meal plan that complements sweet potatoes?
Explore the High-Protein Diet Guide for 2025
🥣 Meal Ideas Based on Cooking Style
🔹 Boiled
-
Mash with garlic and herbs
-
Add to salads or buddha bowls
-
Mix into a veggie stew
🔹 Baked
-
Stuff with black beans + avocado
-
Make sweet potato “toast” slices
-
Serve with grilled chicken or salmon
🔹 Steamed
-
Blend into smoothies
-
Use in baby puree
-
Dice into quinoa bowls
👨🍳 Affiliate CTA: Simplify Healthy Cooking
Want faster prep without sacrificing nutrition? We’ve tested dozens of kitchen tools. Here are our favorites:
-
Top Air Fryer Picks
See pricing and reviews on the official site → LiveSmart Health Cooking Tools -
Gut Health Supplements for Carb-Heavy Diets
Check this recommended tool here → LeanBiome
🔗 Internal Links Used:

Chapter 6: Sweet Potato FAQ – Your Top Questions, Answered
Got questions about sweet potatoes? You’re not alone. Whether you’re managing your weight, tracking blood sugar, or just want clarity on portion sizes, this section answers the most common, evidence-backed questions around sweet potato nutrition.
Let’s cut through the myths and get to the facts.
❓ Are Sweet Potatoes Good for Weight Loss?
Yes — when prepared correctly and eaten in moderation.
Sweet potatoes:
-
Are low in calories (~86 kcal per 100g boiled)
-
Are high in fiber, which helps with satiety
-
Deliver long-lasting energy without blood sugar spikes
-
Reduce cravings by supporting gut health and insulin balance
📌 Research from the Journal of Medicinal Food found that regular intake of sweet potatoes may contribute to improved blood glucose control and reduced appetite.
💡 Pro Tip: Boil or steam them, avoid frying or sugar-heavy versions like casseroles.
👉 Pair them with workouts for max fat-burn — here’s a home workout plan for beginners you can follow today.
❓ Can Diabetics Eat Sweet Potatoes Safely?
Yes — especially when boiled or steamed.
Unlike white potatoes, sweet potatoes have a lower glycemic index (GI), meaning they cause slower blood sugar increases. Boiled sweet potatoes typically have a GI between 44–61, compared to 78–85 for white potatoes.
✅ Best practices for diabetics:
-
Boil or steam (never fry)
-
Keep portions moderate (½ cup is a good serving)
-
Eat with protein or healthy fat to blunt the blood sugar rise
👉 See our full 2025 Diabetes Management Guide for more smart-carb tips.
❓ How Much Sweet Potato Should I Eat Per Day?
It depends on your goals, but a general guideline:
| Goal | Recommended Portion |
|---|---|
| Weight Loss | ½ cup cooked (100–130g) |
| Muscle Gain | 1 cup cooked (200–250g) |
| Blood Sugar Management | ½ cup, paired with protein/fiber |
| Gut Health Boost | ½–1 cup daily with probiotic foods |
🧠 Portion tip: Think of sweet potatoes as your smart starch, not the star of your plate.
👉 Need gut-friendly balance?
Check this recommended tool here → LeanBiome
❓ Are Sweet Potatoes Keto-Friendly or Low-Carb?
Not really.
Even though sweet potatoes are nutrient-dense, they’re still high in carbs — about 20g per 100g cooked — which can kick you out of ketosis.
❌ Not suitable for:
-
Keto diets
-
Carnivore diets
-
Ultra low-carb phases
✅ Better for:
-
Moderate-carb lifestyles
-
Paleo, Mediterranean, or plant-forward diets
Need alternatives? Try:
-
Cauliflower mash
-
Zucchini noodles
-
Shirataki rice
👉 Explore our Caffeine-Free Coke Alternatives — because your drinks matter, too.
❓ Is the Sweet Potato Skin Healthy?
Yes — if it’s organic or well-washed.
The skin is a rich source of fiber, potassium, and antioxidants. It can support digestion, gut health, and even immunity.
💡 Eat the skin if:
-
The potato is scrubbed clean or organic
-
It’s baked or steamed (not deep-fried)
-
You’re pairing it with herbs, oil, or spices to add flavor
Bonus: You’ll waste less food and get more nutrients.
👉 Check out our Top Superfoods to Burn Fat for more “skin-on” foods worth eating.
❓ Can Sweet Potatoes Cause Bloating or Gas?
In some cases, yes — especially if:
-
You suddenly increase your fiber intake
-
You eat them with lots of fat or sugar
-
You already have a sensitive gut (IBS, SIBO, etc.)
Solutions:
-
Start with smaller portions
-
Chew thoroughly
-
Combine with gut-friendly foods like ginger or probiotics
🛒 Need bloating relief that works with high-fiber foods?
Discover this affordable solution today → LeanBiome
Or check our Best Probiotics for Bloating in 2025
❓ What’s the Best Time of Day to Eat Sweet Potatoes?
There’s no “bad” time — but for optimal performance:
-
Morning or lunch → for stable energy
-
Pre-workout → for slow-burning fuel
-
Post-workout → to replenish glycogen
-
Dinner → if paired with lean protein and portion-controlled
Sweet potatoes digest slower than white rice or bread, making them ideal for curbing late-night snacking too.
👉 Need meal inspo? Our Healthy Chicken Recipes pair perfectly with roasted sweet potatoes.
🔗 Internal Links Used:
Chapter 7: Final Takeaways — Is Sweet Potato Nutrition Worth the Hype?
After all the breakdowns, benefits, and how-to guides, here’s the honest bottom line:
Sweet potatoes aren’t a trend. They’re a nutritional upgrade — and one of the most affordable, versatile, and research-backed whole foods you can add to your plate.
✅ Why Sweet Potatoes Deserve a Spot in Your Weekly Routine
Let’s recap what you’re actually getting:
-
✅ Steady energy from complex carbs
-
✅ Immune support via Vitamin A & C
-
✅ Improved digestion through fiber and prebiotics
-
✅ Blood sugar balance (especially when boiled or steamed)
-
✅ Versatility across every meal: breakfast to dinner
-
✅ Better satiety than most starchy foods — helping with fat loss
And unlike trendy supplements or imported superfoods, sweet potatoes are:
-
Easy to find
-
Easy to cook
-
Easy to afford
🛠 Practical Tips to Get the Most from Sweet Potato Nutrition
Here’s how to turn knowledge into action:
🔹 1. Cook smart
Use boiling or steaming to keep nutrients intact and lower glycemic impact.
🔹 2. Portion right
Aim for ½–1 cup per meal, especially if tracking weight or carbs.
🔹 3. Pair wisely
Add lean protein and healthy fat to create complete, blood-sugar-friendly meals.
🔹 4. Rotate varieties
Try orange and purple sweet potatoes to get the full range of antioxidants.
🔹 5. Supplement when needed
Pair your sweet potato-rich diet with gut and metabolism support for amplified results.
👉 Discover this affordable solution today → LeanBiome
(Improves digestion, supports healthy metabolism — works well with fiber-rich foods like sweet potatoes.)
👉 See pricing and reviews for LiveSmart cooking tools → LiveSmart Health Tools
🧠 What’s the Best Way to Start?
If you’re new to sweet potatoes, start small:
-
Add them to a stir-fry or salad
-
Replace white rice or bread once per day
-
Roast in batches for meal prep
-
Try a smoothie with steamed cubes for breakfast
Want even easier swaps and clean meals? Check out our Healthy Chicken Recipes that pair perfectly with sweet potatoes.
💬 Real Reader Win
“I swapped sweet potatoes for my usual bagels and pasta for two weeks. Not only did I lose 4 pounds, I stopped feeling bloated all the time. This one change made a big difference — and I’m not going back.”
– Amara S., Chicago
📚 Want to Go Deeper?
Here’s where to keep learning:
✅ Affiliate Disclosure & Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. If you click and make a purchase, we may earn a small commission — at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products or services we personally trust, use, or have independently reviewed.
Medical Disclaimer: The content in this article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not constitute professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your diet, supplement regimen, or exercise routine.
Please log in to access your exclusive content.
Don’t have an account? Click the “Register” button below to sign up.










